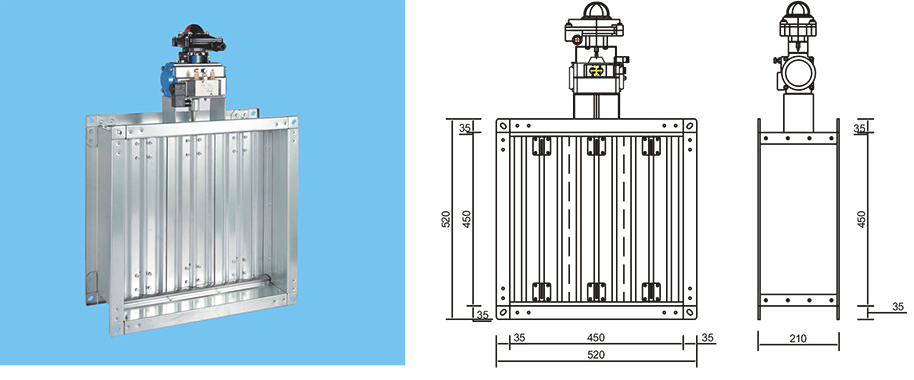
Product overview
Pneumatic damper is a device that uses compressed air as a power source to control the opening, closing, or regulating of the medium flow rate through changes in air pressure. The following is a detailed introduction about pneumatic dampers:
Pneumatic damper, also known as pneumatic ventilation butterfly valve, is a device for controlling the flow of air or gas in pipelines by dividing and merging or switching the flow direction.
Function description
Using solenoid valves to control the opening or closing of cylinders
● Adopting a dual cylinder structure for pulling and pulling
Electromagnetic valve controls opening and closing
Pneumatic switch controls opening and closing
● Drawing style dual cylinder structure
● Plug in structure
● 1. Open the intake valve. Close the intake valve
● 2. Open the single acting ventilation valve and close the shut-off valve
● 3. Display valve position open and closed
● 4, ⑤⑥ Feedback on signal ② ③ Feedback off signal
● 5. Adopting a 2-position 3-way solenoid valve
6. NL power on valve opens, power-off valve closes
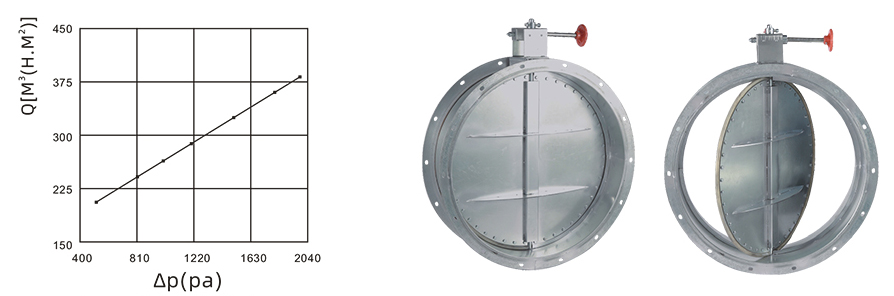
|
Static pressure difference on both sides of the valve plate △ P (pa) |
500 |
800 |
1000 |
1200 |
1500 |
1800 |
2000 |
Air leakage rate per unit area of valve disc
Q[M³(H.M²)] |
Standard allowable value |
≤625.0 |
≤820.8 |
≤934.2 |
≤1038.4 |
≤1181.9 |
≤1313.7 |
≤1396.5 |
|
Inspection value |
203.5 |
243.8 |
263.6 |
290.8 |
324.9 |
353.6 |
389.0 |
|
Inspection conclusion |
Qualified (ordinary type) |
|
Valve opening angle α ° |
90 |
75 |
60 |
45 |
|
Project |
|
Resistance coefficient ξ |
0.64 |
1.05 |
3.80 |
10.70 |
|
Air volume regulation ratio μ (%) |
100.0 |
78.1 |
41.1 |
24.5 |
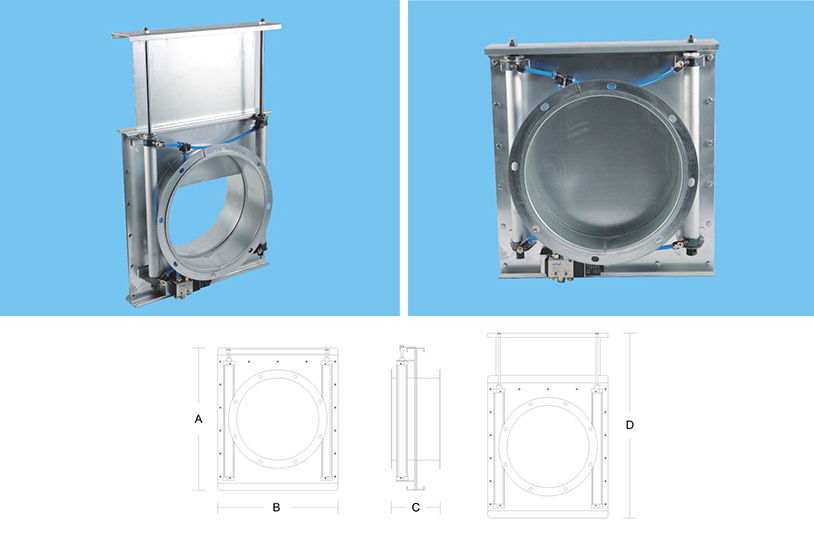
Table of dimensions and parameters for pneumatic plug in valve
|
Specifications |
Outer plate thickness |
Insertion board thickness |
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
f100 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
230 |
230 |
170 |
|
|
f150 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
290 |
330 |
170 |
|
|
f200 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
340 |
380 |
170 |
|
|
f250 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
390 |
430 |
170 |
|
|
f300 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
440 |
480 |
170 |
|
|
f400 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
540 |
590 |
170 |
|
|
f500 |
2.0 |
3.0 |
640 |
690 |
170 |
|
|
f600 |
3.0 |
3.0 |
740 |
790 |
170 |
|
Working principle
Air supply: Pneumatic dampers require a stable compressed air source, usually provided by an air compressor and transported to the valve through pipelines.
Execution mechanism: The execution mechanism of pneumatic dampers is usually a cylinder or diaphragm actuator. When compressed air enters the actuator, it will push the cylinder piston or diaphragm to move.
Valve core action: The movement of the actuator drives the connected valve core or valve plate to move, changing the opening of the valve and controlling the flow rate of the medium.
Control signal: The operation of the pneumatic damper can be achieved through manual operation, solenoid valve control, or more complex control systems such as PLC. These control systems send signals to solenoid valves or other types of pilot valves to control the entry or exit of compressed air into the actuator.
Characteristics and advantages
Energy saving and environmental protection: Pneumatic dampers control the opening and closing of valves through air pressure, without additional energy consumption, and have good energy-saving and environmental protection effects.
Easy to operate: The pneumatic damper is easy to operate, just control the supply of compressed air to achieve valve opening and adjustment.
Quick response: Pneumatic dampers have a fast response speed and can quickly open and close the valve, making them suitable for situations that require quick action.
Safe and reliable: Pneumatic dampers are powered by compressed air and pose no risk of electrical sparks, making them suitable for applications with high explosion-proof requirements.
Strong adaptability: The pneumatic damper has a compact structure, light weight, easy installation, and can adapt to harsh environments such as high temperature, humidity, and dust.
Structure and type
Structure: Pneumatic dampers usually adopt a new structural form of welding midline disc plates and short structural steel plates, which is compact, lightweight, and easy to install. There are no connecting rods or bolts inside the body, making it reliable and with a long service life.
Type: According to different usage scenarios and functions, Pneumatic dampers can be divided into various types, such as regulating type, quick opening type, quick closing type, etc. Adjustable pneumatic dampers can receive signals from the system and adjust the opening of the valve based on the magnitude of the signal; Quick opening and quick closing pneumatic dampers are suitable for situations that require quick opening or closing.
Application scenarios
Pneumatic dampers are used in situations where air volume or direction needs to be adjusted, especially in industrial environments with high explosion-proof requirements, rapid action, or harsh environments. For example:
Petrochemical industry: used in pipeline systems in refineries, chemical plants, and other places to control the flow of media such as oil products and chemical raw materials.
Coal mining industry: used in the ventilation system of coal mines to ensure air circulation and safety inside the mine.
Food and pharmaceutical industry: used in the production process of food, beverage, pharmaceutical and other industries to control the flow and direction of media, ensuring the hygiene and safety of the production process.
Installation and maintenance
Installation:
Before installing the pneumatic damper, the pipeline should be cleaned and purged to ensure that there are no impurities inside the pipeline.
Check whether the model and parameters of the pneumatic damper meet the on-site installation requirements and technical requirements.
Install in the direction indicated by the arrow on the pneumatic damper body (downstream installation), ensuring good sealing at the connection.
maintain:
Regularly inspect the actuator, valve core, and other components of the pneumatic damper for damage or wear, and replace them promptly if necessary.
Clean the surface and internal components of the pneumatic damper to remove impurities such as dust and oil.
Regularly check whether the air supply is stable to ensure the normal operation of the pneumatic damper.