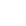
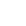Product overview
A sealed damper is a device that can regulate, control, or close the airflow in an air duct. It adjusts the air volume by changing the opening of the valve, thereby achieving the goal of controlling indoor temperature, humidity, and air quality.
Major function
Adjust air volume: Adjust the air flow through the air duct by changing the opening of the valve according to actual needs.
Maintain airtightness: When the valve is closed, ensure the airtightness of the pipeline system to prevent gas leakage.
Balance system pressure: In the ventilation system, the pressure of each branch pipeline is balanced by adjusting the opening of the air valve.
Prevent airflow backflow: In specific situations, such as when the wind direction changes, prevent airflow from backflow into the pipeline system.
Working principle
A closed air valve usually consists of a valve body, an actuator, and a control system. The actuator drives the valve body to open or close according to the instructions of the control system, thereby accurately controlling the airflow through the air duct. The actuator can be in manual, electric, or pneumatic form, among which electric and pneumatic actuators can achieve remote control and automated operation.
Structure and material
Structure: There are various structural designs for sealed dampers, but they usually include valve bodies, valve plates (or valve cores), seals, actuators, and other parts. The valve body is the main frame of the air valve, supporting the entire device and connecting to the ventilation duct; The valve plate (or valve core) adjusts the size of the airflow channel by rotating or sliding; The sealing element ensures the airtightness of the air valve in the closed state; The actuator is responsible for driving the movement of the valve plate (or spool).
Material: The material selection of the sealed damper depends on its usage environment and medium characteristics. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, galvanized sheet, etc. These materials have good corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, and can meet the requirements of different working conditions.
Application scenarios
sealed dampers are used in situations where airflow control and airtightness are required, including but not limited to:
Industrial production: Industrial sites such as chemical and pharmaceutical factories that emit toxic and harmful gases, used to control the amount and flow of gas emissions.
Construction engineering: Used in the air conditioning, ventilation, and smoke exhaust systems of large commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and other places to regulate the mixing ratio of fresh air and return air, ensuring indoor air quality.
Special environments: such as telecommunications cabinet rooms, civil defense engineering, biosafety laboratories, and other places that require high air tightness to prevent the intrusion of external pollutants.
Selection and Installation
Selection: When selecting, factors such as valve size, material, sealing performance, as well as the accuracy and reliability of the actuator need to be considered. At the same time, it is necessary to determine the type of valve (such as regulating type, cut-off type, etc.) and control mode (such as manual, electric, pneumatic, etc.) based on specific usage scenarios and requirements.
Installation: During the installation process, ensure that the valve is tightly connected to the air duct to avoid air leakage. Meanwhile, it is also necessary to pay attention to the flow direction and installation direction of the valve to ensure its normal operation. For electric or pneumatic actuators, it is also necessary to connect the corresponding power or gas source and perform necessary debugging and testing.
Maintenance
In order to ensure the long-term stable operation of the sealed damper, regular maintenance and upkeep are required. Specific measures include:
Regular inspection: Check the appearance, seals, and actuator components of the valve for damage or wear, and replace them promptly if necessary.
Cleaning and maintenance: Clean the dust and dirt on the surface of the valve to prevent them from affecting the flexibility and sealing performance of the valve. For electric or pneumatic actuators, it is also necessary to clean the dust and debris inside.
Lubrication and maintenance: For components that require lubrication, such as transmission mechanisms, bearings, etc., an appropriate amount of lubricant should be added regularly to reduce friction and wear.